International trade involves the movement of goods across different territories by Road, Rail, Air, Sea and Inland Waterways. Over the years, global trade has increased tremendously through the proliferation of Trade Agreements amongst countries. Bilateral and Multilateral Trade Agreements are made with the intention of growing trade volumes through the reduction of Tariff and Non-tariff Barriers to trade. Rules of Origin are a very critical component of trade agreements as we shall see below.
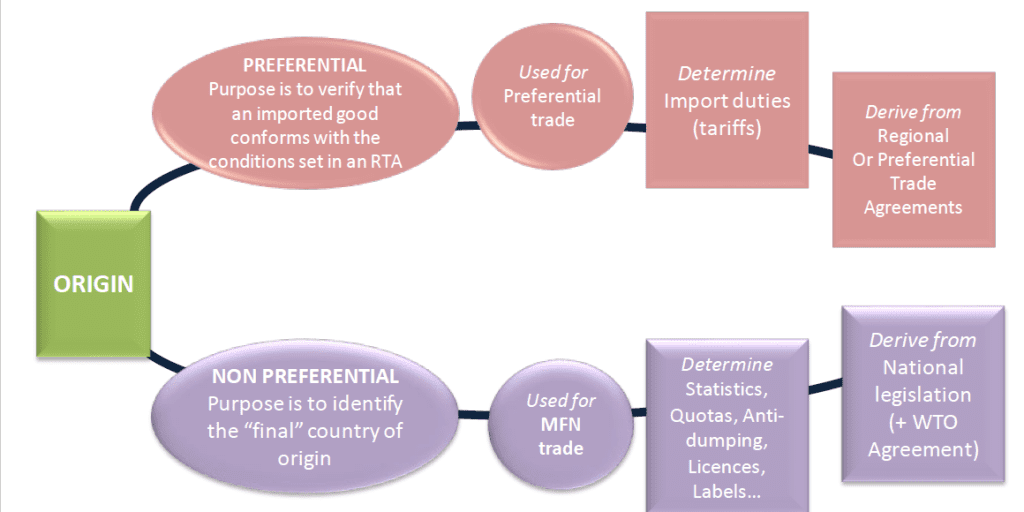
Rules of Origin (ROO) can be defined as the rules, laws and procedures that are used to determine the national source of a product/good. Under ROO, goods are regarded to be from a certain Territory if they meet the Origin Criteria and are accompanied by a Valid Certificate of Origin/Origin Declaration as per conditions set out in the Trade Agreement.

Functions of Rules of Origin
1. Preferential tariff Treatment to goods i.e. Reduction or Elimination of Customs Duties
2.Collection of Trade Statistics
3. Antidumping and Countervailing duty Measures
4.Quotas
5.Sanitary and Phytosanitary inspections
6.Country of Origin marking/Labeling
Types of Rules of Origin
1.Preferential Rules of Origin
This type of ROO is derived from preferential Trade Agreements and confers Preferential tariff treatment on goods that meet Origin criteria and are issued with a valid Certificate of Origin (COO). Preferential tariff treatment means the reduction or elimination of Customs duties for Imports that meet origin criteria.
Preferential trade agreements have several forms:
A .Reciprocal Trade regimes:
This is where all parties reduce tariffs with respect to each other eg
Free Trade Agreements, Free Trade Zones, Economic Partnership Agreement, Customs Unions, etc.
Bilateral Agreements (EU-Chile, US -Korea) or Regional Agreements (e.g. NAFTA, COMESA, ASEAN, EAC, GCC etc.)
For Instance, A registered Manufacturer in Kenya imports wheat (Tariff Heading 10.01) mills it into Flour (Tariff Heading 10.01) and exports to a Consignee in Juba, South Sudan. Under EAC Rules of Origin, the Wheat Flour is deemed to have met Origin Criteria through Substantial Transformation (Change in Tariff Heading) and should be accompanied by a Valid EAC COO to enjoy zero Import Duty in South Sudan. This is because both countries are members of the EAC Customs Union and are bound by EAC Rules of Origin.
On the other hand, when a Furniture company in Kenya imports Equatorial Teak (Wood) that is Wholly Obtained from South Sudan. The EAC ROO evidenced by a Valid EAC COO shall allow the Importer in Kenya to enjoy zero Import duty rates on the goods.
B. Non-Reciprocal” or “Unilateral” Trade Regime:
This is where only one of the parties reduces or eliminates its tariffs with respect to imports from the other parties, while the others continue to maintain tariffs eg Developed or developing countries’ “General System of Preferences”, GSP (e.g. US African Growth and Opportunity Act (AGOA) for Sub-Saharan African countries, EU “Everything But Arms (EBA)”, China’s preferences for least developed countries, etc.
For Instance, A manufacturer of Cotton suits in Kenya can access the US Market duty free through AGOA so long as the conditions of the agreement are met i.e AGOA ROO. On the other hand, importation of goods of USA Origin into Kenyan territory are done at Most Favoured Nation (MFN) Import duty rates.
2.Non-Preferential Rules of origin
As the name suggests, goods imported under this ROO do not enjoy Preferential Tariff Treatment.
Trade among Members of the WTO is usually conducted based on the Most Favoured Nation principle. In respect to import duties, this means that WTO Members must, in the absence of preferences or exceptions, apply to each other the same import duty for like products.
Non-preferential rules of ROO ARE NOT used to implement trade preferences. Instead, they are used in the context of Other Trade Policy Measures such as Import Quotas, Antidumping, Countervailing, Food and Health(sanitary)/Safeguard measures, etc. They are also used to indicate the country of origin on labels (consumer policies) and to collect trade statistics for National Planning.
Source: WTO
Proof of Origin
There are two ways of proving the Origin (Economic nationality) of goods:
1.Certificate of Origin issued by a Competent Authority eg Customs, Chamber of Commerce at the Country of Export
2.Origin declaration issued by the Exporter of the goods.
It is vitally Important to note that the rules of origin which apply to an international transaction are always that of the IMPORTING country: it is the importing country that sets the conditions for entry of goods in its territory. This is why rules of origin have a direct impact on MARKET ACCESS conditions.
As discussed above, it is clear that Rules of origin are a critical Component in any Trade Agreement and should be mastered by Importers, Exporters, Cargo Consolidators, Freight Forwarders, Customs Administrations etc
Contact us for any enquiries on Rules of Origin and Customs Clearance in the East African Community (EAC)
Email: solutions@goliath-africa.com
Tel no: +254(0)739057747/+254(0)738057935
Whatsapp/Wechat: +254739057747







Comments4
Insightful..
We are glad that you gained some knowledge from our blog.
hello!,I like your writing so much! proportion we communicate more about your post on AOL?
I need a specialist in this space to unravel my problem.
May be that's you! Looking ahead to peer you.
Also visit my blog; find some
Kindly send a formal email to solutions@goliath-africa.com